


It also promotes the development of the immune system (thanks to the creation of antibodies), it is involved in the formation of hormones, enzymes and collagen (protein that creates bones, cartilage and connective tissues).įoods rich in lysine are fish, eggs, cheese, soy grains, potatoes, yeast and dairy. Lysine is involved in the metabolism of lipids, making them used as an energy source. Lysine intervenes in the formation of L-carnitine, which is a compound that allows the circulation of oxygen in muscle tissues. įoods rich in tryptophan are turkey, chicken, beef, fish, soy grains, rice, some nuts and cheese. The deficit of this amino acid generates insomnia, depression and weightloss. It also intervenes in tolerance to pain, so it is used by athletes who undergo intense physical activities. For this reason, said amino acid is used in pharmaceuticals antidepressants and in sedative and hypnotic pills. Tryptophan helps in the formation of serotonin and melatonin, substances that regulate the sleep cycle. Some foods rich in this amino acid are beef, pork and fish, eggs, yogurt, cheese, soy products and some nuts.
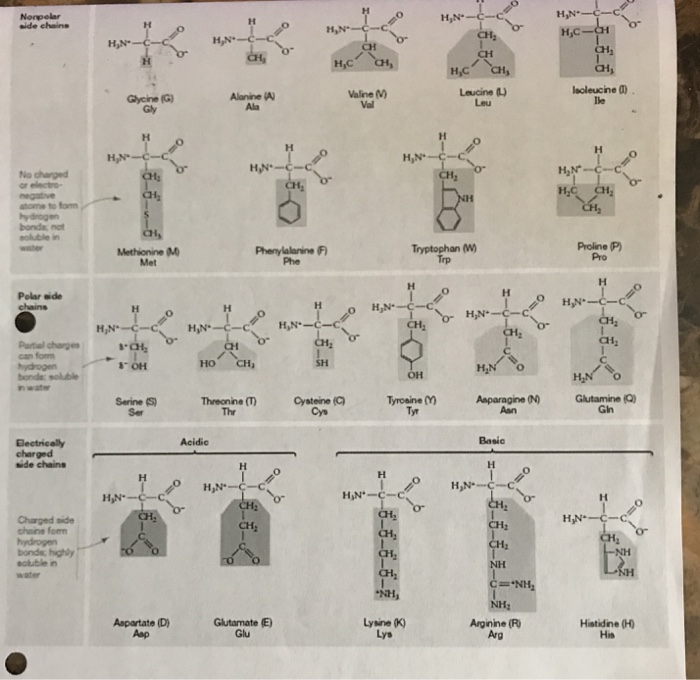
Phenylalanine deficiency can lead to depression, loss of appetite, cognitive problems (confusion, loss of memory), lack of energy, decreased alertness, among others. Similarly, phenylalanine is involved in the formation of thyroid hormones. Phenylalanine is necessary for the formation of chemicals used by the brain (neurotransmitters and hormones), such as dopamine, noradrenaline Y adrenalin. Phenylalanine is an amino acid found in three forms: L-phenylalanine (naturally synthesized), D-phenylalanine (artificially synthesized) and DL-phenylalanine (a mixture of the two above). The 20 amino acids and their main functions 1- Phenylalanine The non-essential amino acids are 12: glycine, alanine, serine, cysteine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, asparagine, glutamine, arginine, tyrosine, proline and histidine. In general terms, the functions of amino acids are as follows:ġ-Regulate the sleep cycle and wakefulness.ģ-Stimulate the synthesis of muscle proteins.Ĥ-Improve the circulation of oxygen in the muscles.ĥ-Regulate brain activity (such as alertness and feelings of depression)ħ-The essential amino acids are eight: phenylalanine, tryptophan, lysine, methionine, threonine, isoleucine, leucine and valine. Foods with the highest content of essential amino acids are meats (including fish), eggs, dairy products, nuts and some vegetables.įor their part, non-essential amino acids are those that can be produced by the human body (specifically by the liver) without the help of external agents.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
